Here’s an interesting question: “What mortgage has the best interest rate?”
Before we dive in, “best” questions are always a bit difficult to answer universally. What’s best to one person could be the worst for another. Or at least not quite the best.
This is especially true when discussing mortgage questions, which tend to be a bit more complex.
But we can still talk about what makes one mortgage rate on a certain product better than another.
In a recent post, I touched on the different mortgage terms available, such as a 30-year, 15-year, and so on.
That too was a “best” article, where I attempted to explain which mortgage term would be best in a particular situation.
Related to that is the associated mortgage interest rate that comes with a given loan term. Together, they can drive your mortgage product decision.
Longer Loan Term = Higher Mortgage Rate

- The longer the fixed-rate period, the higher the interest rate
- This compensates the lender (or their investor) for taking on more risk
- Because they’re agreeing to a certain interest rate for a longer period of time
- For example, a 30-year fixed loan will price higher than a 15-year fixed loan
Now I’m going to assume that by best you mean lowest, so we’ll focus on that definition, even though it might not be in your best interest. A lot of puns just happened by the way, but I’m trying to ignore them.
Simply put, a longer mortgage term generally translates to a higher mortgage rate.
So a 10-year fixed-rate mortgage will be much cheaper than a 40-year fixed loan for two borrowers with similar credit profiles and lending needs.
In addition, an adjustable-rate mortgage will typically be priced lower than a fixed-rate loan, as you’re guaranteed a steady rate for the full term on the latter.
This all has to do with risk – a mortgage lender is essentially giving you an upfront discount on an ARM in exchange for uncertainty down the road.
With the fixed-rate loan, nothing changes, so you’re paying full price, if not a premium for the peace of mind in the future.
If the interest rate is fixed, the shorter term loan will be cheaper because the lender doesn’t have to worry about where rates will be in 20 or 30 years.
For example, they can offer you a lower mortgage rate on a 10-year term versus a 30-year term because the loan will be paid off in a decade as opposed to three.
After all, if rates rise and happen to triple in 10 years, they won’t be thrilled about your super low rate that’s fixed for another 20 years.
That’s all pretty straightforward, but knowing which to choose could be a bit more daunting, and may require dusting off a mortgage calculator.
[How to get the best mortgage rate.]
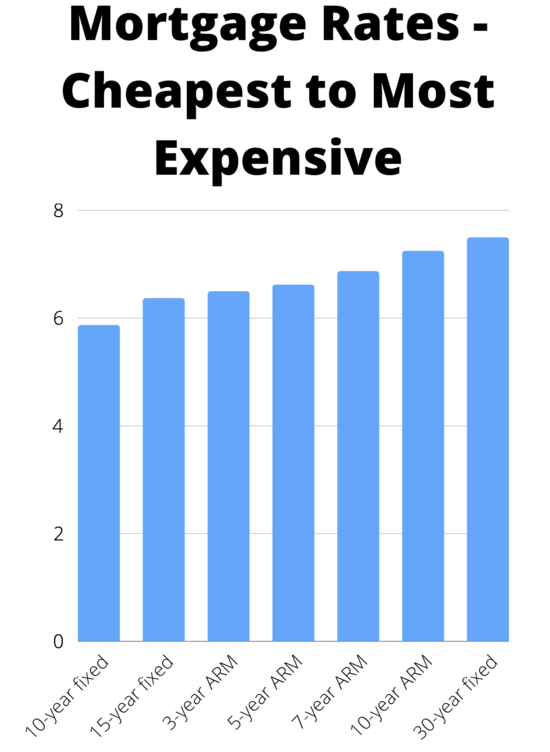
Mortgage Interest Rates from Cheapest to Most Expensive
- 1-month ARM (cheapest)
- 6-month ARM
- 1-year ARM
- 10-year fixed
- 15-year fixed
- 3-year ARM
- 5-year ARM
- 7-year ARM
- 10-year ARM
- 30-year fixed
- 40-year fixed (most expensive)
This can definitely vary from bank to bank. But it’s a rough order of how mortgage rates might be priced from lowest to highest, at least in my view.
Many lenders don’t even offer all these products, especially the super-short term ARMs. However, you can get an idea of what’s cheapest and most expensive based on its term and/or how long it’s fixed.
The very popular 30-year fixed is currently pricing around 7.375%, while the 15-year fixed is going for 6.50%, per my own research of the latest mortgage rate data.
The hybrid 5/1 ARM, which is fixed for the first five years and adjustable for the remaining 25, might average a slightly lower 6.625% versus the 30-year fixed.
The cheapest mainstream product is the 10-year fixed, which is averaging around 5.75% because the term is so short.
There are many other loan programs, such as the 20-year fixed, 40-year fixed, 10-year ARM, 7-year ARM, and so on.
But let’s focus on the 30-year fixed and 5-year ARM, as they’re the most popular in their respective categories.
You Pay a Premium for the 30-Year Fixed
As you can see, the 30-year fixed is the most expensive in the chart above. In fact, it’s nearly a percentage point higher than the average rate on a 5/1 ARM.
This spread can and will vary over time, and at the moment isn’t very wide with most lenders, meaning the ARM discount isn’t great.
At other times, it might be a difference of one percent or more, making the ARM a lot more compelling.
Anyway, on a $400,000 loan amount, that would be a difference of roughly $200 in monthly mortgage payment and about $12,000 over five years.
For the record, a 3/1 ARM or one-year ARM would be even cheaper, though probably just slightly. And for a loan that adjusts every three years or annually, it’s a big risk in this rate environment.
As mentioned, the low initial rate on the 5/1 ARM is only guaranteed for five years. Then it becomes annually adjustable for the remainder of the term. That’s a lot of years of uncertainty. In fact, it’s 25 years of risk.
The 30-year fixed is, well, fixed. So it’s not going higher or lower at any time during the loan term.
The ARM has the potential to fall, but that’s probably unlikely. And lenders often impose interest rate floors that limit any potential interest rate improvement. Go figure.
What Is the Cheapest Type of Mortgage?
- VA loan (cheapest)
- FHA loan
- USDA loan
- Conforming loan
- Jumbo loan (most expensive)
If we’re talking about types of mortgages, you’ll likely find that VA mortgage rates are the lowest relative to other loan programs.
The reason being is VA loans are government-backed loans and they’ve got the VA’s guaranty if the loan defaults.
In this case, the VA pays the lender, so there’s less risk in making the loan. So despite a 0% down payment, VA loans offer the lowest rates in most cases.
For example, a 30-year fixed VA loan is pricing around 6.75% at the moment, whereas a conforming loan backed by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac is priced closer to 7.50%.
That’s a pretty significant difference in rate, which will equate to a lower payment, even if putting zero down on a home purchase.
The next cheapest type of mortgage is the FHA loan, which is also government-backed and comes with mortgage insurance (MIP) that is paid upfront and monthly by the borrower.
This too protects lenders in the case of borrower default and results in lower mortgage rates.
FHA mortgage rates tend to be about a half a percentage point lower than a comparable conforming loan, so maybe 7% if conforming loans are priced at 7.50%.
Then there are USDA loans, which are also government backed, but might price a little higher at say 7.25%.
That brings us to conforming loans, which price above all the government-backed loans mentioned.
Beyond that, you’ve got jumbo loans, which are typically more expensive than conforming loans. However, this can flip-flop at times based on market conditions.
Also note that interest rate is just one piece of the pie. There are also closings costs and mortgage insurance premiums that can drive the mortgage APR higher.
So when comparing conventional loans vs. FHA loans, it’s important to consider all the costs.
Combining loan program with loan type, a 15-year fixed VA loan would technically be the cheapest.
So What’s the Best Mortgage Rate Then?
- The best mortgage rate is the one that saves you the most money
- Once you factor in the monthly payment, closing costs, and interest expense
- Along with what your money could be doing elsewhere if invested
- And what your plans are with the underlying property (how long you intend to keep it, etc.)
The best interest rate? Well, that depends on a number of factors unique to you and only you.
Do you plan to stay in the property long-term? Or is it a starter home you figure you’ll unload in a few years once it’s outgrown?
And is there a better place for your money, such as the stock market or another high-yielding investment?
If you plan to sell your home in the medium- or near-term, you could go with an ARM and use those monthly savings for a down payment on a subsequent home purchase.
Just be sure you have enough money to make larger monthly payments. If and when your ARM adjusts higher if you don’t actually sell or refinance your mortgage before then.
Five years of interest rate stability not enough? Look into 7/1 and 10/1 ARMs, which don’t adjust until after year seven and 10, respectively.
That’s a pretty long time, and the discount relative to a 30-year fixed could be well worth it. Just expect a smaller one relative to the shorter-term ARMs.
But if you simply don’t like stress and/or can’t take chances, a fixed-rate mortgage is probably the only way to go.
Short-Term Mortgages Like the 15-Year Fixed Are the Best Deal
If you’ve got plenty of money and actually want to pay off your mortgage early, a 15-year fixed will be the best deal. And as noted, a 10-year fixed can be even cheaper.
The shorter term also means less interest will be paid to the lender. The downside is the higher monthly payment, something not every homeowner can afford.
This is especially true now that mortgage rates are a lot higher than they were two years ago.
One option is to go with a 30-year fixed and pay extra each month. This allows it to operate like a 15-year fixed, with added flexibility.
As a rule of thumb, when interest rates are low, it makes sense to lock in a fixed rate, especially if the ARM discount isn’t big.
But mortgage rates are no longer cheap.
An ARM Could Work, Just Know the Risks
Conversely, if interest rates are high, taking the initial discount with an ARM may make sense.
In the event rates have fallen when it comes time to refinance (after the initial fixed period comes to an end), you could make out really well.
And even if rates fall shortly after you get your mortgage, you can refinance to another ARM, thereby extending your fixed period.
Or simply trade in your ARM for a fixed-rate mortgage if rates get really good during that time.
The other side of the coin is that rates could keep climbing. This could put you in a tough spot if your ARM adjusts higher and interest rates aren’t favorable at the time of refinancing.
Ultimately, you’re always taking a risk with an ARM. But you could also be leaving money on the table with the fixed-rate loan, especially if you don’t keep it anywhere close to term.
Either way, watch those closing costs and be wary of resetting the clock on your mortgage if your ultimate goal is to pay it off in full.
In the end, it may all just come down to what you’re comfortable with.
For many, the stress of an ARM simply isn’t worth any potential discount. So perhaps a fixed mortgage is “best,” even if they aren’t cheap anymore.
Read more: Which mortgage is right for me?
- Rocket Mortgage Completes Redfin Takeover, Offers $6,000 Home Buyer Credit - July 1, 2025
- Mortgage Rates Quietly Fall to Lows of 2025 - June 30, 2025
- Trump Wants Interest Rates Cut to 1%. What Would That Mean for Mortgage Rates? - June 30, 2025


What’s the rate on the 40 year fixed right now?
Likely quite a bit higher than a 30-year fixed (maybe 1% or more) because they are only offered by select portfolio lenders and non-agency lenders. They were mostly banned due to QM rule.
Which is why I was surprised you mentioned them. They seem dang near impossible to find and I assume are very edge case type products.
Just want to present the complete picture of loan offerings. They do exist and illustrates how longer duration costs more.